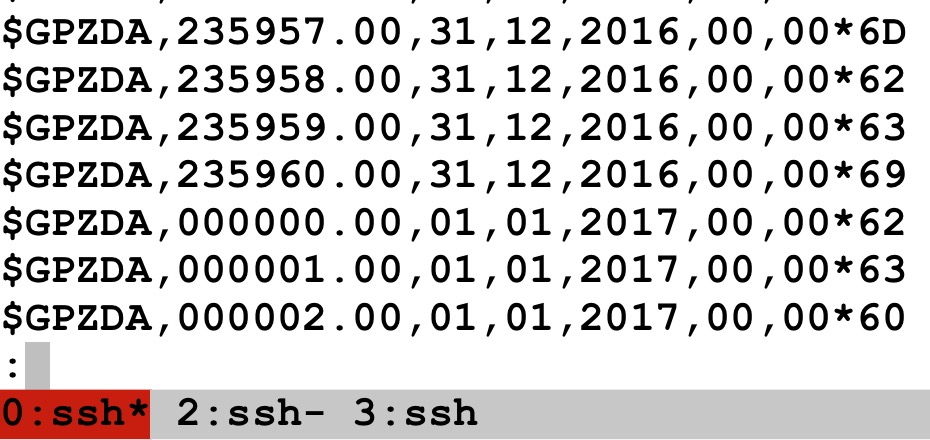
235960 – 23:59:60 – the leap second added.
UTC (based on solar mean) – TAI (based on atomic clock) = -37 seconds
Happy New Year 2017 UTC

235960 – 23:59:60 – the leap second added.
UTC (based on solar mean) – TAI (based on atomic clock) = -37 seconds
Happy New Year 2017 UTC
I don’t really know when, I suspect around 4.8.0-30 or a bit earlier that kernel boot time has noticeably increased.
There is a bug/regression report on launchpad
Quick fix ? Try 4.9 mainline ppa.
Results from my systemd-analyze:
4.8.0-32 = 12.331s4.9 = 5.041sปี 2529 อยู่ ม.2 ไม่เคยเล่นเกม ไม่เคยใช้โปรแกรมสำเร็จรูป แตะคอมพิวเตอร์ครั้งแรกก็หัดโค้ดเลย
มันคือเครื่อง VTech Laser 200 (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VTech_Laser_200)
ROM เป็น BASIC interpreter สมัยนั้นเรียกของพวกนี้ว่า home computer ก็ไม่แน่ใจว่าเครื่องนี้เป็นของใคร แต่มันวางอยู่ที่บ้านที่ไปอาศัยอยู่ช่วงนั้น หัดจากคู่มือของเครื่อง (ภาษาอังกฤษ) หนังสือตัวอย่างโปรแกรมที่แถมมา จนเขียน BASIC เป็น
ม.ปลาย ที่โรงเรียนสอนภาษา Logo .. ช่วงนั้นมีเครื่อง PC ที่บ้านแล้ว รับจ้างเขียนโปรแกรม พิมพ์รายงาน
ป.ตรี รับจ้างเขียน inventory ให้ รพ.ศรีนครินทร์ (Clipper/Netware) โปรเจคจบเขียน C/C++ เป็นโปรแกรมบน Windows
ป.โท ระหว่างเรียนเขียน C, C++, CLIPS, LISP, Prolog, OCaml, Smalltalk, YACC, Lex, Java
ป.เอก เข้ารีต F/OSS ทำ packages ให้ LinuxTLE เขียนตาม upstream ใช้ภาษาไหนก็โค้ดภาษานั้น coding style แบบไหนก็ต้องตามนั้น เพลินมากจนเกือบเรียนไม่จบ 555+
อืม .. เดี๋ยวนะ ผมอยู่สาย sysadmin/ops มาตั้งแต่เรียน ป.ตรี นะหนิ (^^)a
Same tools, same OS as $5/month: DigitalOcean vs Vultr
dd write bs=4k count=10k 100k 1M
403 398 184 MB/s
dd read bs=4k 2.0 GB/s
sysbench --test=cpu --cpu-max-prime=10000 run 17.9875 sec.
stress-ng --cpu 1 --cpu-method all -t 30 94.22 ops/sec
The disk performance is comparable to those of DO/Vultr. But, even equipped with 2 x 64-bit x86 processor, CPU performance is lower than single core on $5/mo. VPS of DO/Vultr.
Since I use them as a web server, so I run ab -n500 -c500 requesting phpinfo() ..
phpinfo() Vultr: 2102.08 req./sec Scaleway: 1543.10 req./sec
YMMV.
Tools: dd, sysbench, stress-ng. I know, you’d say they are NOT benchmark tools. I don’t care, I just need quick tests.
Here we go:
dd write bs=4k count=10k 100k 1M do: 350 465 424 MB/s vultr: 699 538 466 MB/s
dd read bs=4k do: 475 MB/s vultr: 2.7 GB/s
sysbench --test=cpu --cpu-max-prime=10000 run do: 14.2562 sec. vultr: 13.7561 sec.
stress-ng --cpu 1 --cpu-method all -t 30 do: 154.15 ops/sec vultr: 186.38 ops/sec
/me .. goes vultr.
16.04.1 ออกมาได้ประมาณหนึ่งสัปดาห์ 14.04 ก็เริ่มจะ upgrade กันได้ วันนี้สั่ง do-release-upgrade เรียบร้อยดี
ลง PHP7 เพิ่ม / เอา PHP5 ออก / แก้ไข socket path = เว็บกลับมาปกติ
ง่ายเกินไปนะ :P
วันนี้ ceph เดี้ยง
สืบพบว่ามาจาก monitor node 2 ใน 3 ตัว .. ทั้งสองตัว เป็น VM connect ได้ daemon running แต่ disk ของตัว host เป็น read-only .. พอ monitor พยายามบันทึกข้อมูลลง disk ไม่ได้มันก็ค้าง พอ monitor ค้าง ceph cluster ทั้งก้อนหยุดทำงาน
ได้ใช้ท่า troubleshooting: stop monitor / dump monmap / ลบ monitor node ที่ใช้งานไม่ได้ออกไปจาก monmap / inject monmap ตัวใหม่เข้า monitor node ที่ใช้งานได้
restart monitor
คืนชีพ (^^)v
You can always do this.
# echo "- - -" > /sys/class/scsi_host/host#/scan
I’ve been using Graylog in production for awhile. It’s a great log analysis tool, backed by elasticsearch. Conceptually, graylog is pretty much like splunk. I consolidate approximately 170-200 million log messages to graylog everyday. So, I need to optimize them well enough.
Few days ago, I started to use Fortigate extractors from a git repo. It uses regex, and it is very slow. So I (have to) write my own extractors. I write Grok pattern, and keep rewriting until I could cover all messages I need to extract. Then, I started to optimize the pattern. The result is quite good though. I could reduce extractor time from more than 100,000 usec to about 100 usec.
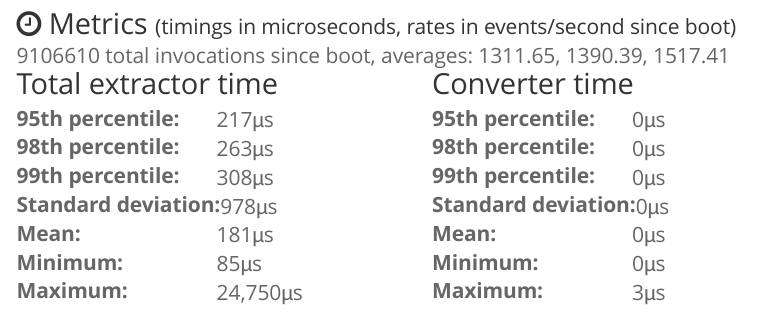
Yes, that’s approximately 1000x times faster. It’s definitely not perfect though, but it works for me. If you think it might be good for you, you can download my Fortigate content pack here.
Enjoy :)
dnsmasq is the default DNS resolver if you use NetworkManager. It runs pretty well most of the time. When it doesn’t, you would not be able to access the Internet if you need to resolve names.
I’m not a fan of dnsmasq, and if you – like me – want to disable it, just edit
/etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf
and remove/comment
dns=dnsmasq
Restart NetworkManager, it will use traditional faithful method of /etc/resolv.conf.